Introduction to Reverse Engineering & Solving a Windows CRACKME
Reverse engineering is a powerful skill for anyone interested in software development or cybersecurity. By examining the inner workings of a software application, you can identify vulnerabilities, modify the software for a specific purpose, or gain a deeper understanding of its design. In this post, we’ll explore the basics of reverse engineering by walking through the process of solving a CRACKME program using static analysis tools/
Some CRACKME programs are designed to be difficult to reverse engineer or modify, making them a great challenge for those interested in honing their skills in reverse engineering and static analysis. In this post, we’ll provide an introduction and demonstrate how to solve a CRACKME program step-by-step.
What tools do you need? #
Before we dive into the reverse engineering process, we’ll need to make sure we have the right tools. Here are the tools you’ll need for this tutorial:
- Cheat Engine
- Our CRACKME program we will be focusing on
- IDA Pro or IDA Freeware
- Visual Studio or almost any C++ compiler (optional for later)
Getting started with the CRACKME program #
To start off, we’ll focus on a simple CRACKME program from crackmes.one, a popular website for practicing reverse engineering skills. This particular CRACKME program is designed to be challenging and is a great way to practice your skills in static analysis and reverse engineering. If you want to follow along with this tutorial, you can download the CRACKME program from this link.
Step 1: Opening the CRACKME program #
First, let’s open the CRACKME program. When we open the program, we’ll be prompted with a message asking us to enter a key.
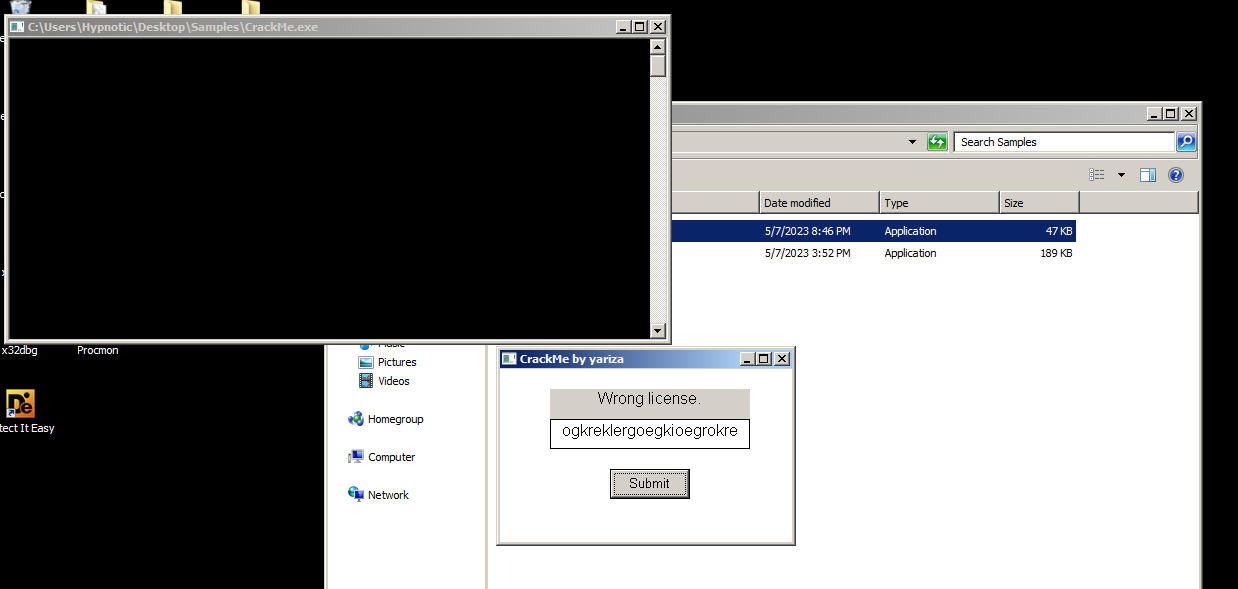
Since we don’t have the key, we can’t proceed any further. This is where our tools come in handy.
Step 2: Using the program with Cheat Engine #
Cheat Engine is a powerful tool that allows us to analyze and modify the memory of a running program. We can use it to identify where the the check is in memory, so we can patch it to bypass the check.
To use Cheat Engine, we’ll need to open the CRACKME program and then open Cheat Engine. Once Cheat Engine is open, we’ll need to select the CRACKME program from the list of processes. 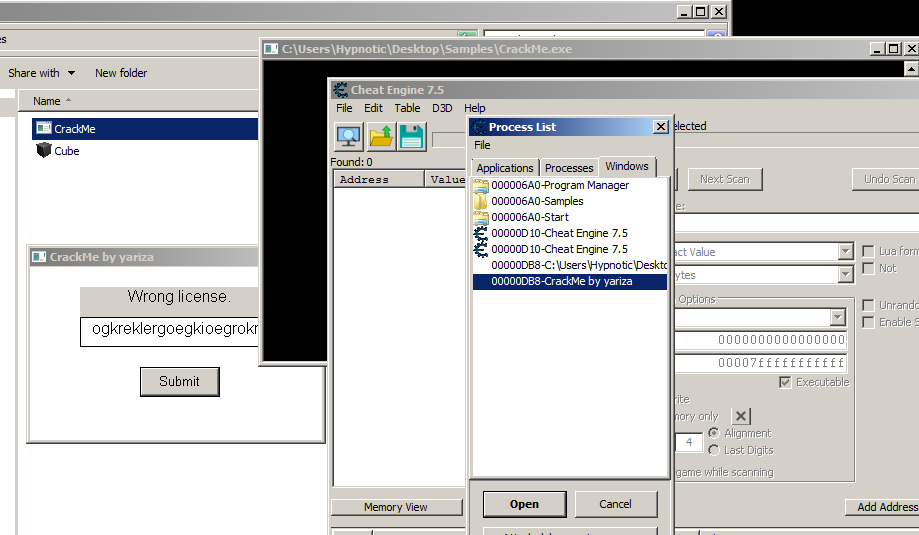
Now, open Memory View and on “View” you will see “Referenced strings” and upon opening this window you will see all of strings used from the data segment referenced inside memory which is the .text segment.
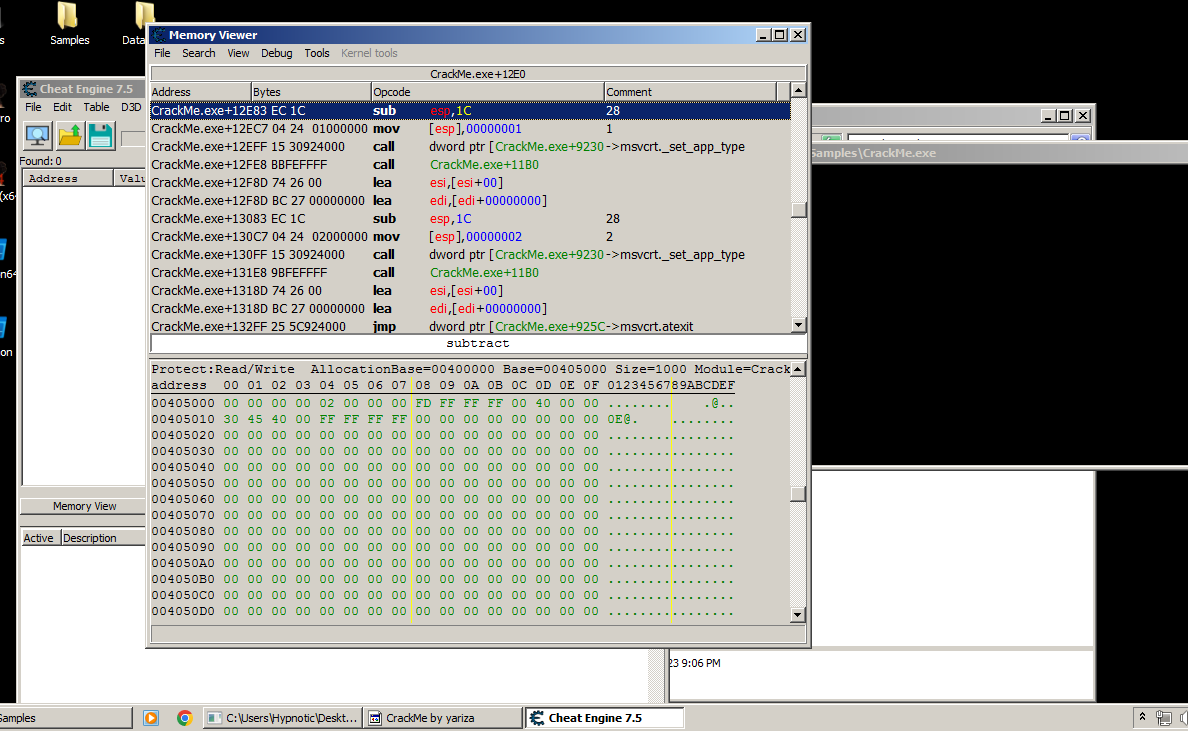
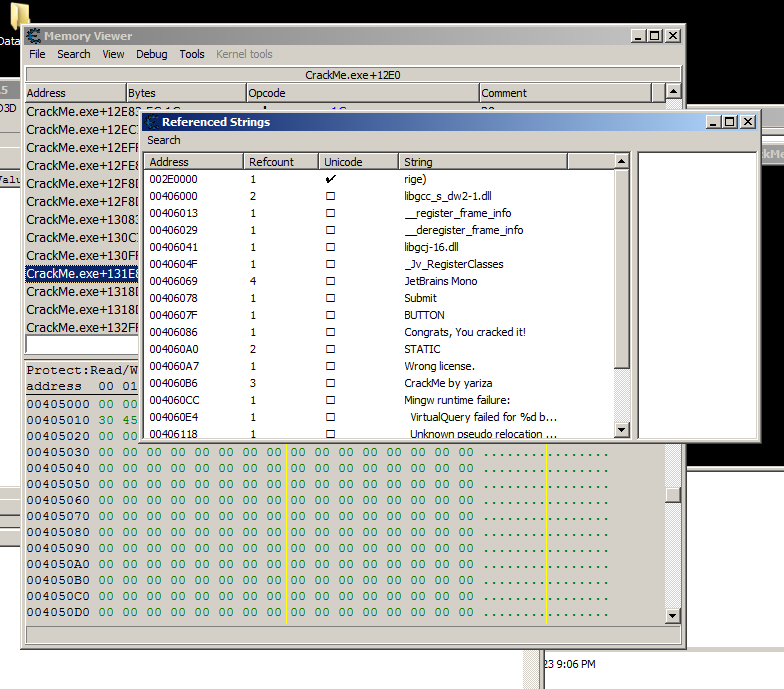
What is a segment? #
A segment is a named section of the file’s memory layout. The PE file format divides the file’s memory into several logical parts, each with a specific purpose. These parts are known as sections or segments, and each section has a unique name and attributes.
For example, the .text segment contains the executable code of the program. This segment is typically read-only and is loaded into memory when the program is executed. The .data segment contains the program’s initialized data, such as global variables and static data. The .rdata segment contains read-only data, such as string literals and other constants.
Other common segments in a executable include .rsrc, which contains resources such as icons and dialogs, and .reloc, which contains relocation information to adjust the program’s memory addresses at runtime.
Common things with most keygen programs or most likely difficult CRACKME programs is that they will have their own segment depending on if they pack the executable with Themida for example which contains .boot and .themida.
Step 3: Analyzing with IDA Pro #
Upon firing up your favorite disassembler we are going to use IDA Pro which is used in this tutorial. Start by opening your file and waiting for it to finish analyzing. Once it has finished, click SHIFT + F12 to open the “Strings” window.
Now we are going to search for the following strings referenced in the program like we just did in Cheat Engine which is using CTRL + F to find strings. After searching for “Wrong License.” double clicking it will lead to the string stored in data along by cross referencing it pressing X on your keyboard will lead to the function that uses the string. 
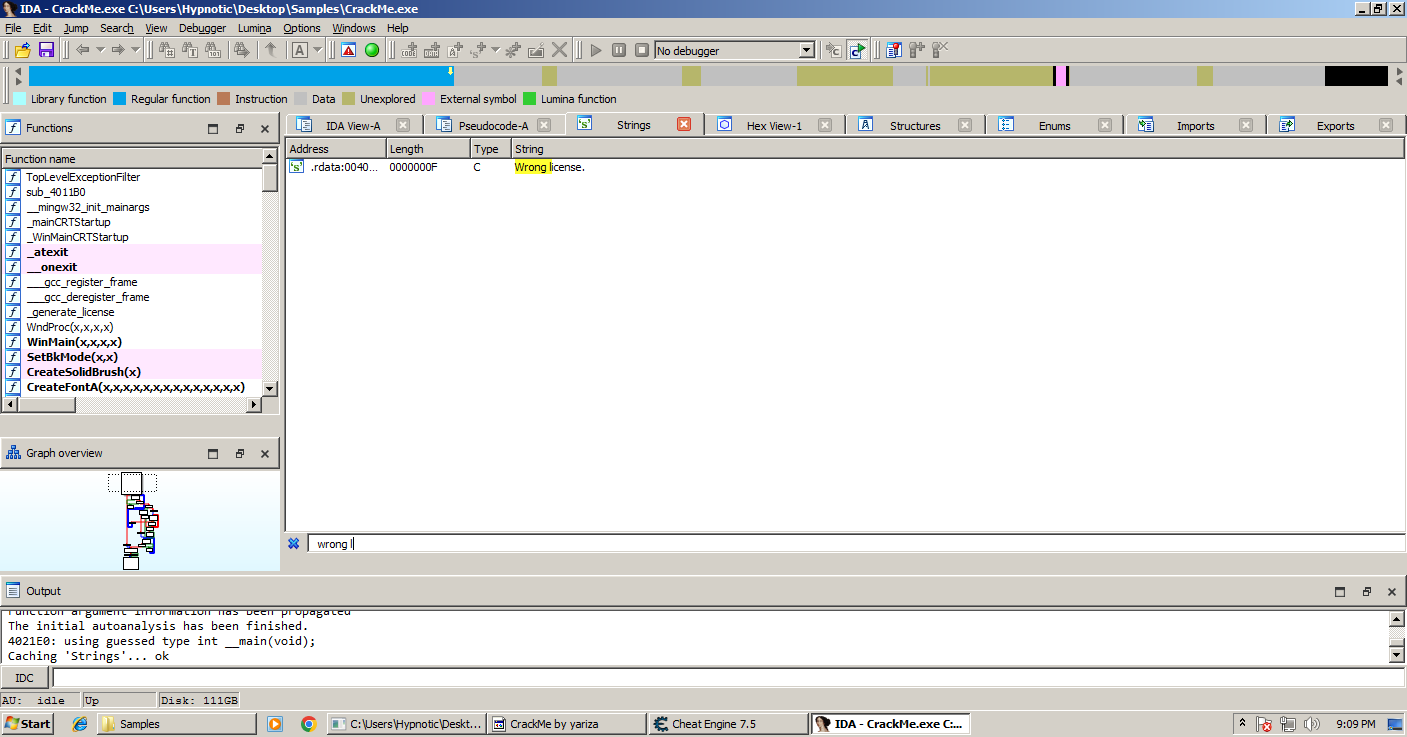
Scrolling up reveals another string reference which shows if the license is correct or not, since it’s a simple comparison check a way to patch the program is to save the address that upon execution will say that the license key is correct.
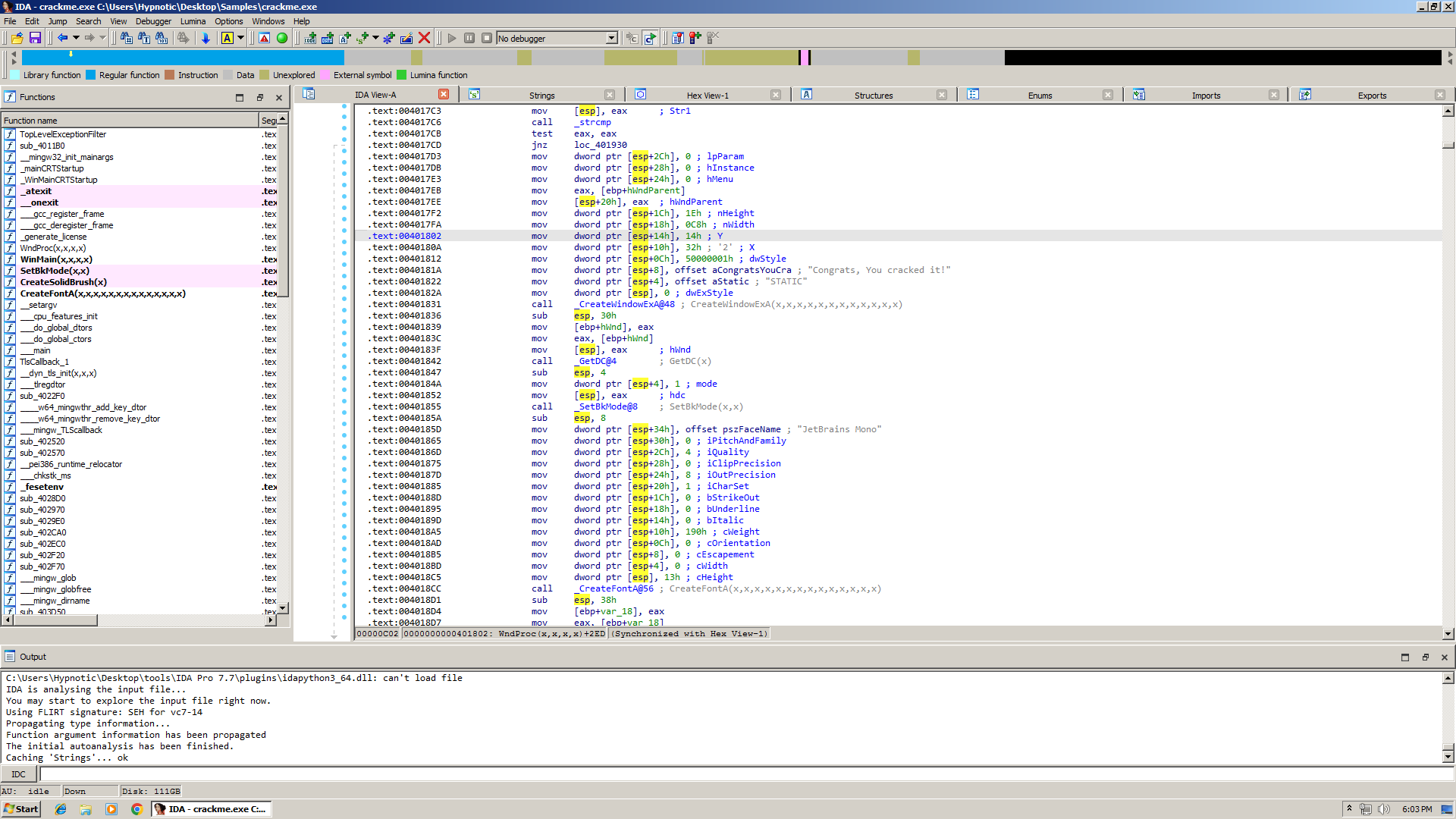
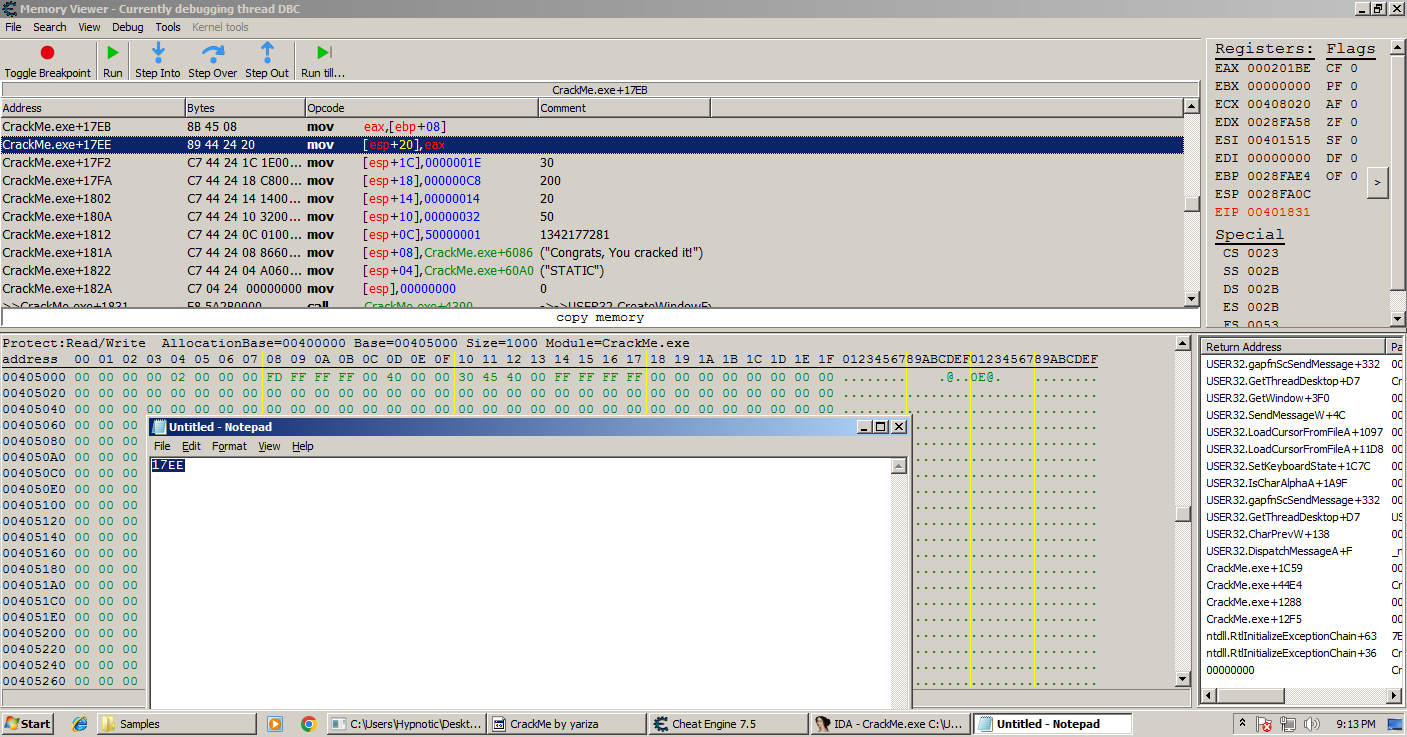
As we breakpoint on the address that gets executed when we enter the wrong key it appears to be hit, we can either place a jmp to the address that tells you if it’s a valid license.
Using Cheat Engine’s assembler we can jmp to the address as we saved earlier to the one that will let us defeat the crackme, and when we enter any other license you can see that it says “Congrats, you cracked it!”
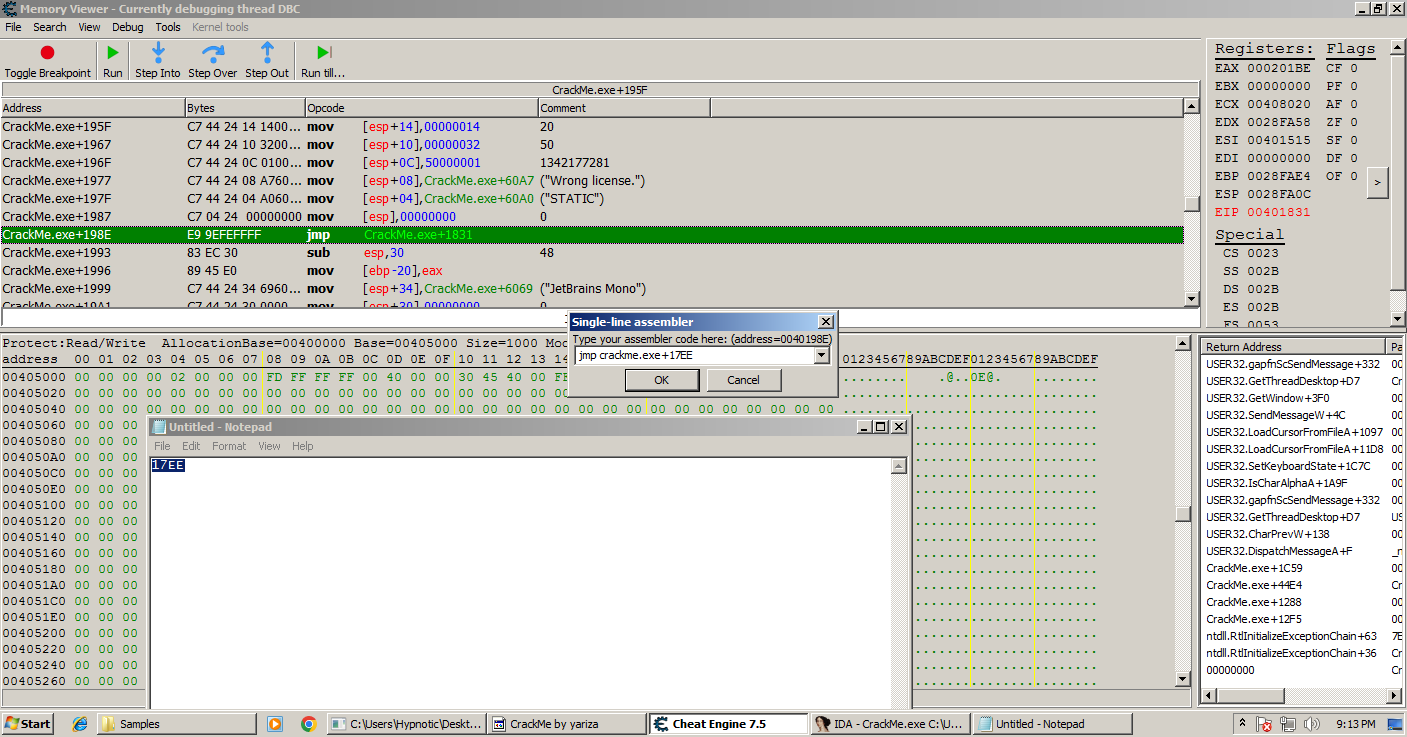
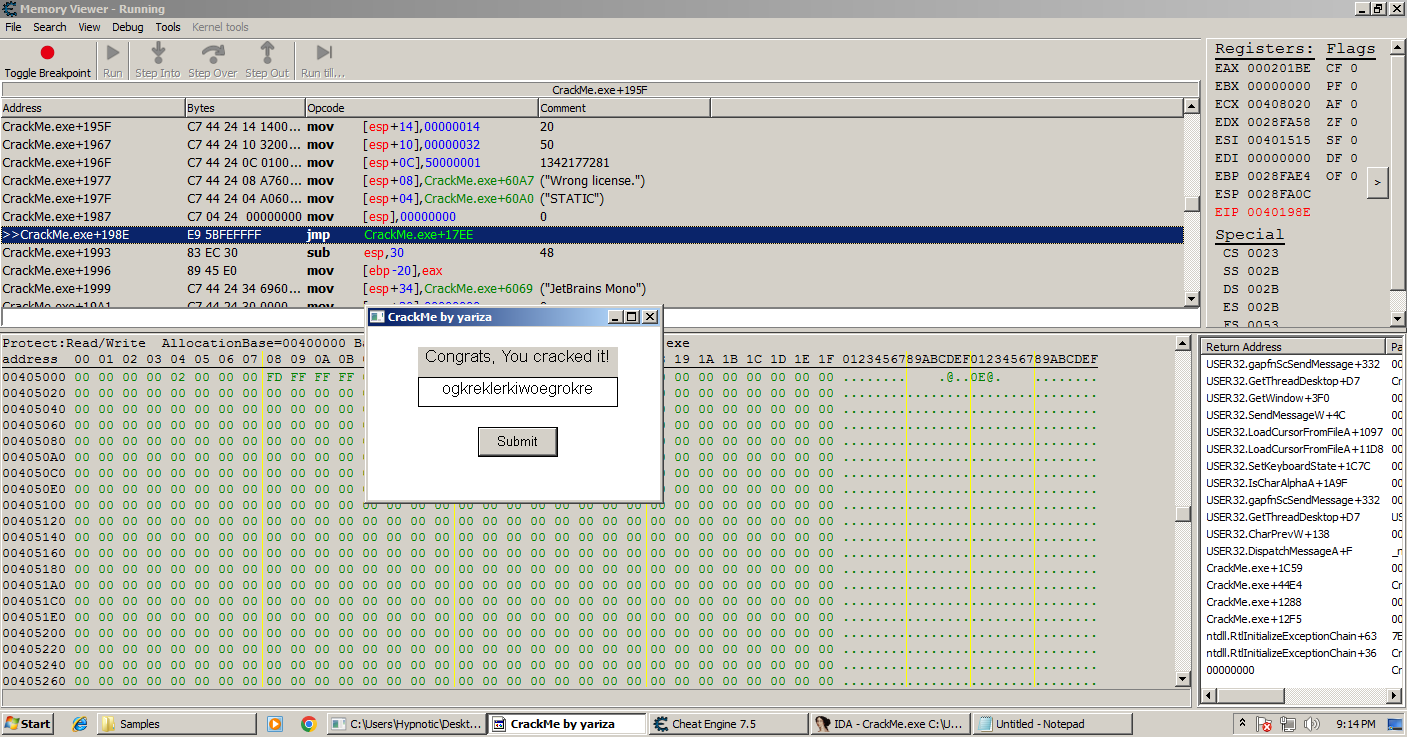
And congratulations, you have figured out how to byte patch a program!
Final NOTE: This method won’t exactly work on every program since they will be built differently along with having virtualization, mutation and others. So don’t expect yourself to crack anything huge.